The rubber molding process creates various rubber products like tires, seals, and gaskets. It is a versatile method that can produce parts with different shapes and sizes with high precision.
The process involves shaping rubber compounds into molds and then curing them to achieve the desired properties. Here are the main steps involved in the rubber casting process:
Designing Rubber Molds
The rubber mold design process starts with material selection based on the product’s purpose and environment. Silicone is used for high-temperature applications, while nitrile suits oil-resistant products.
Precision in design can help to accommodate potential shrinkage or deformation. Designing involves creating a blueprint or 3D computer-aided design (CAD) model of the desired part.
The design must take into consideration factors such as material properties, product dimensions, and production volume. The mold designer creates a detailed mold layout that specifies where to place gates, vents, and cavities for optimal flow of rubber material.
They also consider draft angles, parting lines, and other features that help with the release of the finished product from the mold.
Vulcanization in Rubber Molding
Vulcanization transforms raw, natural rubber into durable and resilient products by subjecting it to heat and pressure. During the rubber molding process, vulcanization occurs after someone places the uncured rubber into the mold.
Professionals use heat and pressure to trigger a process where the rubber molecules link together, forming a robust and steady structure. This makes the rubber stronger and more durable. Vulcanization also helps to improve the elasticity and resistance of rubber products.
Compression Molding
Compression molding is a standard method used in rubber molding to create a wide range of products, such as seals, gaskets, and tires. To create a rubber product, professionals place the uncured rubber into a heated mold cavity and then increase the pressure.
It allows the rubber to flow and take the shape of the mold. After vulcanization occurs, the molded rubber product is removed from the mold and cooled before it is trimmed and finished. Compression molding is ideal for creating large rubber parts with high strength and durability.
Transfer Molding
Transfer molding is also a popular method used in rubber manufacturing. It involves placing uncured rubber into a heated chamber and then using a piston to transfer it into the mold cavity. The rubber is then subjected to heat and pressure, which causes it to flow into the mold.
Once vulcanization occurs, the molded product is removed from the mold and cooled before completion.
Transfer molding allows for more precise control over the amount of rubber used in each part, resulting in less material waste. It also enables manufacturers to produce consistent, high-quality rubber products with intricate designs.
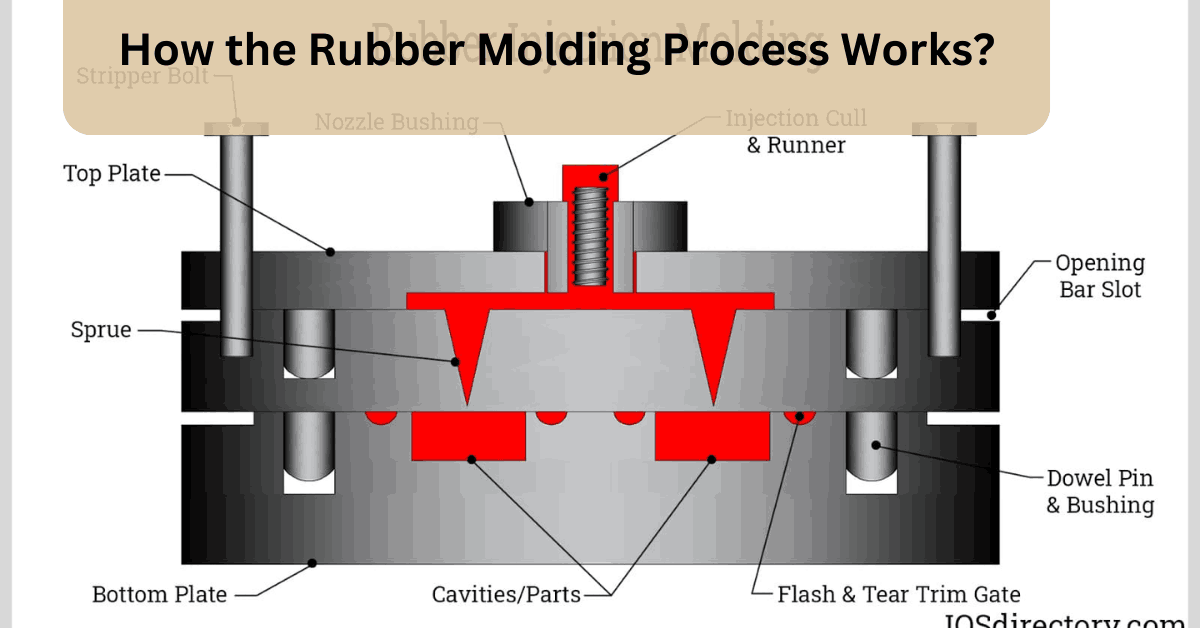
Injection Molding
The injection molding process begins with feeding plastic granules into a heated barrel to melt them. After cooling and solidification, a professional ejects the molded product from the mold.
Injection molding also allows for the use of different types of rubber materials, such as thermoplastic elastomers, to create products with varying properties.
It offers manufacturers flexibility and versatility in producing a wide range of rubber components for various industries such as automotive, medical, and consumer goods. Injection molding is an efficient method that can produce large volumes of rubber parts in a short time. Rubber molding requires accurate mold design and strict control of temperature, pressure, and injection speed to get consistent quality products.
Discover the Versatility of Rubber Molding
The rubber molding process involves using pressure and heat to shape uncured rubber into high-quality products. Three commonly used methods are compression molding, transfer molding, and injection molding. Each is suitable for different types of rubber products.
To learn more about these techniques and how they can benefit your business, consult with a professional in the rubber industry.